Domain scheduler
In this section, we are going to explain the worflow of domain scheduler.
The domain scheduler is responsable to retrieve pending jobs related to domain drivers and lunchs the other crawling DAGs. We have 2 schedulers that uses the same operator: One for Microsoft Teams and Google Chat and the other one for Google Classroom.
The jobs in crawlserver mongo db are presented as documents saved if different collection based on the task we want to accomplish. Each pending job is a document that verify the following conditions :
- Task: equal to the task we want to lunch
- State: should be pending or failed
- Execution_date: should be older than datetime.now()
Microsoft Teams and Google Chat Scheduler¶
The firgure below presents the workflow for domain scheduler
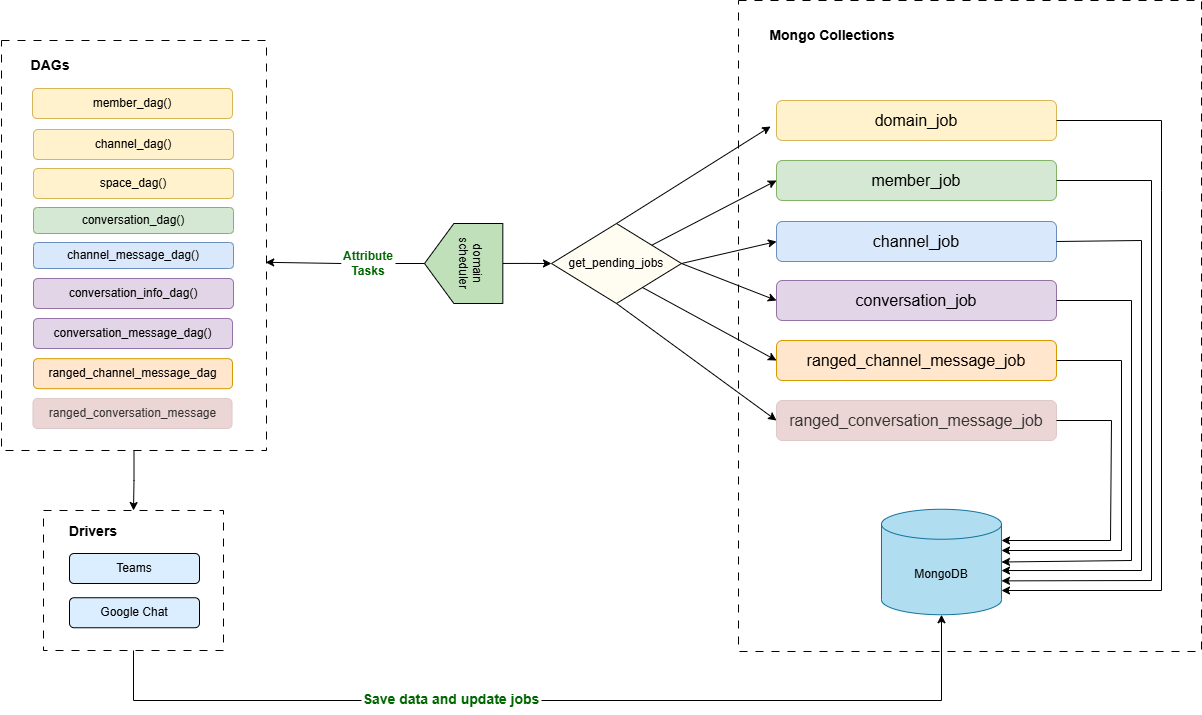
The domains scheduler dag is the main dag that is responsible for retrieving the pending jobs and launch the other dags for Microsoft Teams and Google Chat jobs. It is lunched each 15 minutes.
Each job is related to a specific task. The current available tasks are :
- Member : to collect the list of members in a domain Teams
- Channel : to collect the list of channels in a domain Teams
- Space : to collect the list of GoogleChat Spaces and their members
- Conversation : to collect the list of conversations of a Team member
- Conversation_info : to update the information of a given conversation (list of members, name,...)
- Conversation_message : to collect the messages in a conversation starting from a given date
- Channel_message : to collect the messages in a channel starting from a given date
- Ranged_conversation_message : to collect the messages in a conversation between two dates
- Ranged_channel_message : to collect the messages in a channel between two dates
Google Classroom Scheduler :¶
The firgure below presents the workflow for Google Classroom scheduler
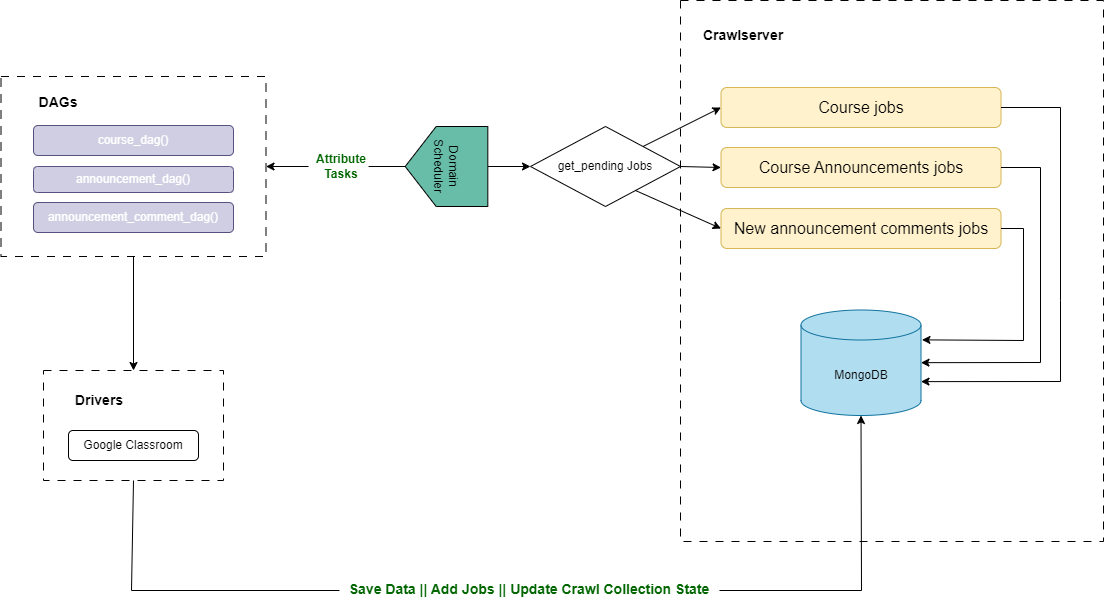
The google classroom scheduler dag is the main dag that is responsible for retrieving the pending jobs and launch the other dags related to Google Classroom. It is lunched each 4 hours.
Each job is related to a specific task. The current available tasks are :
- Course : to collect the list of courses with their members
- Announcement : to collect the list of course announcements
- Announcement Comments : to collect the list of comments that belongs to course announcements
Worklow Explanation:¶
In this part, we are going to explain the pipeline of the schedulers
1. Scheduler Initialization¶
The previously presented schedulers domain_scheduler and google_classroom_scheduler rely both on a same custom operator: DomainSchedulerOperator. Each DAG defines a schedule:
- domain_scheduler: runs every 15 minutes to handle Microsoft Teams and Google Chat
- google_classroom_scheduler: runs every 4 hours for Google Classroom
When a DAG is triggered, it instantiates the DomainSchedulerOperator, which initializes:
- self.dag_url: endpoint for launching other DAGs
- self.schedulerhook: a MongoDB hook (
SchedulerHookDomain) that handles the communication with Mongo DB - self.tasks: a dictionary mapping platforms to supported task names
This setup occurs in the operator’s init method
2. Fetching Enabled Platforms¶
The scheduling logic begins in the execute method of DomainSchedulerOperator
The first step is to retrieve all enabled platforms using:
enabled_platforms = self.schedulerhook.get_enabled_platforms()
3. Retrieving Domains with Valid Settings and Credentials¶
We are going to retrieve for each platform the enabled domains with their settings and credentials using the method get_domains_by_platform(platform_id)
This function performs a MongoDB aggregation pipeline that joins multiple collections:
Lookup to domain_setting¶
{
"$lookup": {
"from": "domain_setting",
"localField": "_id",
"foreignField": "domain_id",
"as": "settings"
}
}
Lookup to domain_credential¶
{
"$lookup": {
"from": "domain_credential",
"localField": "credential_id",
"foreignField": "_id",
"as": "credentials"
}
}
Filter Out Domains with Missing Data¶
{
"$match": {
"$expr": {
"$and": [
{ "$gt": [{ "$size": "$settings" }, 0] },
{ "$gt": [{ "$size": "$credentials" }, 0] }
]
}
}
}
Project Required Fields¶
{
"$project": {
"_id": 1,
"identifier": 1,
"platform_id": 1,
"settings": { "$arrayElemAt": ["$settings", 0] },
"credential": { "$arrayElemAt": ["$credentials.credential", 0] }
}
}
4. Validating Contract Periods¶
Befor lunching the crawl we need to check if the current date is withing the start and end contract date
settings.get('contract_start_date') <= datetime.now() <= settings.get('contract_end_date')
5. Preparing Task Batches¶
As we are working on a real case scenario. We are expected to have many pending jobs so instead of lunching them together we are going to proceed per batch to avoids APIs requests limits. So we need to configure a suitable batch for each task:
batch_dict = self.schedulerhook.get_batch_dictionnary(settings)
This dictionary maps each task to its specific batch size as defined in domain_setting.
Example:
{
"conversation_message": settings.get('nb_batch_conversation_message'),
"channel": settings.get('nb_batch_channel'),
}
6. Fetching Pending Jobs per Task¶
To retrieve the pending jobs for each task we have we use the function get_pending_jobs_per_domain_task(task_name, domain_id, batch). This function:
- Retrieves the appropriate MongoDB collection from
self.task_collection_name - Executes an aggregation pipeline:
Match Stage¶
{
"$match": {
"enabled": true,
"state": { "$in": ["pending", "failed"] },
"domain_id": <domain_id>,
"task": "<task_name>",
"execution_date": { "$lte": <current_datetime> },
"active": true
}
}
Sort and Limit¶
{ "$sort": { "priority": 1, "modified_at": 1 } }
{ "$limit": <batch> }
7. Triggering the Corresponding DAG¶
If jobs are found, the function run_dag(dag_id, data) is called. It:
- Generates a POST URL:
url = f"{self.dag_url}{dag_id}/dagRuns"
- Builds a request payload:
{
"conf": {
"domain": <domain_data>,
"jobs": <list_of_jobs>,
"platform": "<platform_name>",
"dag_run_id": "external_trigger__<timestamp>"
},
"execution_date": "<timestamp>"
}
- Sends the request with credentials from
airflow.cfg
Any errors are logged and wrapped in a custom DauthDagRunException.